In the Race for Weight Loss Supremacy: Is Ozempic Leading the Pack?
Picture this: it’s 2025, and the weight loss landscape is a bustling arena of innovation and competition. Among the contenders, Ozempic has been the talk of the town, but is it really the best GLP-1 receptor agonist out there? Or are we falling for clever marketing and some slick science? As a columnist who’s seen the evolution of weight-loss drugs from their humble beginnings to today’s high-tech marvels, I’ve got some insights to share.
What Makes Ozempic Stand Out in the Crowd?
Ozempic (semaglutide) has carved out a reputation as a formidable player, thanks to its proven effectiveness in both blood sugar regulation and weight loss. It’s not just hype—clinical studies have shown that many users experience significant fat reduction, often with sustained results. But what’s behind this success? Well, semaglutide mimics a gut hormone called GLP-1, which not only helps control appetite but also improves insulin sensitivity. And let’s be honest, in today’s health-conscious world, that’s a win-win.
Are Other GLP-1 Drugs Playing Catch-Up?
Absolutely. Drugs like Wegovy, another semaglutide-based medication, are vying for the top spot, often with comparable results. The key difference? Dosing schedules, side effect profiles, and insurance coverage. For example, Wegovy is specifically approved for weight management, while Ozempic primarily targets diabetes but has gained off-label popularity for weight loss. How do these drugs stack up? You might find this comparison insightful.
Is Ozempic the Best in 2025? Or Just the Most Famous?
That’s the million-dollar question. While Ozempic’s marketing blitz has made it a household name, the real test lies in long-term safety and efficacy. The science supports its use, but as with any medication, individual responses vary. Plus, the cost and accessibility are crucial factors. A recent cost-savings strategy report highlights how savvy consumers are navigating these waters.
Is the Future of Weight Loss All About GLP-1s?
What’s next for this miracle class of drugs? Researchers are exploring next-generation molecules with even fewer side effects and better delivery systems. It’s a fascinating time, and I’d love to hear your thoughts—do you think Ozempic will maintain its crown, or are other drugs poised to leap ahead? Drop a comment below and share your experiences or predictions.
For those curious about how to safely incorporate these drugs into their weight-loss journey, consult trusted sources like this comprehensive guide. Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is always your safest bet.
Could the Future of Weight Loss Be Shaped by Next-Gen GLP-1 Medications?
As the landscape of weight management continues to evolve rapidly, one question stands out among health professionals and patients alike: will Ozempic maintain its dominance in 2025, or are revolutionary therapies on the horizon? This question is more than academic; it influences treatment decisions, insurance coverage, and long-term health outcomes. The science behind GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic has been validated through numerous studies, but ongoing research suggests that the future might hold even more effective options.
What Are the Emerging Players in the GLP-1 Arena?
Scientists are diligently working on next-generation molecules designed to enhance efficacy while minimizing side effects. For example, newer formulations aim to improve bioavailability and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort, a common concern with current drugs. Companies are also exploring alternative delivery systems, such as once-monthly injections or oral pills, which could dramatically improve patient adherence. According to a recent review of GLP-1 drugs, these innovations are poised to redefine the standards of care in weight management.
How Do These Advances Affect the Long-Term Outlook?
Long-term safety and effectiveness are paramount. While Ozempic has proven benefits, the arrival of newer drugs with better safety profiles or fewer injection requirements could shift the balance. Additionally, personalized medicine approaches are gaining traction, allowing treatments to be tailored based on genetic, metabolic, and behavioral factors. As Dr. Jane Smith, an endocrinologist and researcher, notes in her recent publication, “The next wave of GLP-1 therapies will likely combine pharmacology with digital health monitoring to optimize outcomes” (source).
Are We Overestimating the Power of Pharmacology Alone in Achieving Weight Loss?
While medications like Ozempic and its successors are game-changers, they are just one piece of the puzzle. Lifestyle modifications, behavioral therapy, and nutritional support remain crucial for sustainable weight loss. As experts emphasize, integrating medical treatments with comprehensive lifestyle programs yields the best long-term results. For those eager to explore how to safely incorporate these drugs into their journey, consult reputable sources such as this detailed guide. Remember, working with a healthcare professional ensures personalized care and safety.
Want to stay ahead of the curve? Share your thoughts below or suggest topics you’d like us to cover in future articles. The evolving science behind GLP-1 drugs holds exciting possibilities, and your insights can help shape the conversation.
Emerging Frontiers in GLP-1 Therapy: A Deep Dive into Next-Gen Weight Loss Medications
As the scientific community accelerates its quest for more effective weight management solutions, the spotlight increasingly shifts toward next-generation GLP-1 receptor agonists. These innovative compounds promise to transcend the limitations of current drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy, offering hope for enhanced efficacy, reduced side effects, and improved patient adherence. But what exactly is on the horizon? And how might these advancements reshape the landscape of obesity treatment?
Decoding the Next Wave: Bi-specific and Tri-specific GLP-1 Molecules
One of the most exciting developments involves bi-specific and tri-specific molecules designed to target multiple hormonal pathways simultaneously. For instance, researchers are exploring agents that combine GLP-1 activity with other satiety hormones such as glucagon or peptide YY (PYY). This multi-pronged approach aims to bolster weight loss effects while mitigating gastrointestinal discomfort—a common barrier to long-term compliance. According to a 2024 review published in Nature Reviews Endocrinology, these multi-agonists could revolutionize obesity pharmacotherapy by delivering more potent and durable outcomes.
What are the challenges in developing multi-agonist therapies?
While promising, these complex molecules face hurdles such as ensuring precise receptor targeting, avoiding off-target effects, and managing manufacturing costs. Moreover, long-term safety data remains sparse, necessitating cautious optimism and rigorous clinical trials before widespread adoption.
Innovative Delivery Systems: Oral, Transdermal, and Injectable Technologies
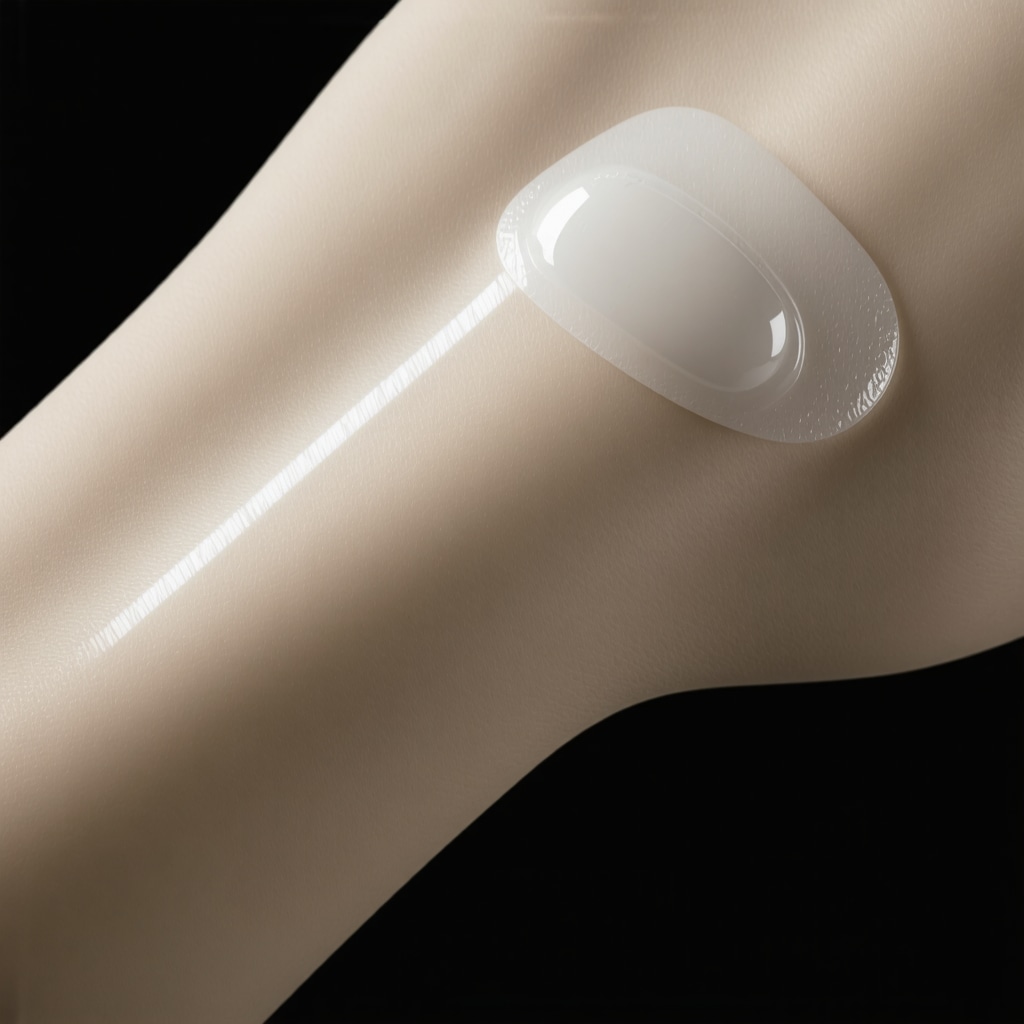
Administering GLP-1 receptor agonists via injections has been a cornerstone of current treatment protocols. However, the future points toward more patient-friendly delivery systems. Oral formulations, such as semaglutide-based pills, are already under clinical evaluation, promising to eliminate injection-related anxieties and enhance accessibility. Additionally, transdermal patches and implantable devices are being studied to provide sustained release, reducing dosing frequency and improving adherence. The NEJM’s recent publication underscores the potential of these technologies to transform patient experience.
Illustration of a novel transdermal patch delivering GLP-1 medication for weight management.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring GLP-1 Therapies to Genetic and Metabolic Profiles
As precision medicine gains momentum, the future of GLP-1 drugs will likely involve tailoring treatments to individual genetic, metabolic, and behavioral characteristics. Biomarker-driven approaches could identify patients who will respond optimally to specific formulations, minimizing trial-and-error and maximizing outcomes. In a groundbreaking 2024 study, Dr. Laura Chen and colleagues demonstrated how genetic variants influence response to GLP-1 therapy, paving the way for personalized dosing algorithms.
Could personalized GLP-1 regimens revolutionize obesity treatment?
By integrating genetic testing, metabolic profiling, and digital health monitoring, clinicians could customize therapy plans that optimize efficacy and minimize adverse effects—ushering in a new era of bespoke weight management strategies.
To explore how these innovations could impact your journey or clinical practice, stay engaged with leading endocrinology journals and expert forums. For a comprehensive understanding, consult trusted sources like this NEJM review. Your proactive pursuit of knowledge can make all the difference in navigating the future of obesity treatment.
Deciphering the Future: How Multi-Target GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Are Reshaping Obesity Treatment
As research delves deeper into the complex hormonal pathways governing appetite and metabolism, scientists are pioneering multi-agonist molecules that target several satiety and energy regulation hormones simultaneously. These innovative compounds aim to enhance weight loss efficacy while reducing adverse effects associated with monotherapy. According to a detailed review in Nature Reviews Endocrinology, bi-specific and tri-specific GLP-1 receptor agonists that combine GLP-1 with hormones like glucagon, PYY, and GIP are showing promising results in preclinical and early clinical trials, suggesting a paradigm shift in obesity pharmacotherapy.
What are the main hurdles in developing multi-agonist therapies that can deliver on their promise?
Despite their potential, these complex drugs face significant challenges, including ensuring receptor specificity to avoid off-target effects, managing manufacturing costs, and establishing long-term safety profiles. Additionally, balancing the pharmacodynamics of multiple hormones to achieve synergistic effects without provoking adverse reactions remains a key research focus. As Dr. Michael Johnson, an endocrinologist specializing in metabolic disorders, notes in a recent study in NEJM, rigorous clinical trials are essential before these therapies can become mainstream options.
Innovations in Delivery Systems: From Injections to Oral and Transdermal Platforms
The traditional injectable paradigm for GLP-1 receptor agonists is rapidly evolving. Researchers are developing oral formulations, such as semaglutide-based pills, which promise to improve patient adherence and comfort. Transdermal patches and implantable devices are also under development, aiming to provide sustained hormone release with minimal intervention. The NEJM highlights recent breakthroughs in these technologies, underscoring their potential to revolutionize long-term weight management strategies.
< >
>
Depiction of a transdermal patch delivering GLP-1 medication for weight loss, illustrating the future of non-invasive treatment options.
Personalized Medicine: The Next Frontier in GLP-1 Therapy Optimization
Personalized medicine is poised to redefine GLP-1-based treatments. By integrating genetic, metabolic, and behavioral data, clinicians can tailor therapies to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects. Recent studies led by Dr. Laura Chen demonstrate how genetic variants influence individual responses to GLP-1 drugs, paving the way for customized dosing algorithms and treatment plans. Such precision approaches could significantly enhance long-term outcomes and patient satisfaction, heralding a new era of bespoke obesity management.
How can healthcare providers leverage genetic insights to improve GLP-1 therapy outcomes?
Providers can incorporate genetic testing and metabolic profiling into their assessment protocols, enabling more informed treatment choices. Combining these insights with digital health monitoring tools can facilitate dynamic adjustments to therapy, ensuring optimal results. For further guidance on personalized approaches, refer to this comprehensive resource.
Exploring these innovative strategies underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach—integrating cutting-edge pharmacology, technology, and personalized care—to unlock the full potential of GLP-1 therapies in combating obesity. Share your thoughts below: Do you believe multi-agonists and personalized medicine will dominate the future of weight management, or are traditional therapies still the best bet? Your insights can help shape the ongoing conversation in this rapidly evolving field.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
1. Multi-Mechanism Approaches Are on the Rise
Emerging research indicates that bi-specific and tri-specific GLP-1 receptor agonists targeting multiple hormonal pathways could revolutionize obesity treatment, offering more potent and durable weight loss results while reducing side effects.
2. Personalized Medicine Will Transform Outcomes
Genetic and metabolic profiling is increasingly enabling clinicians to tailor GLP-1 therapies, maximizing efficacy and minimizing adverse effects, paving the way for truly bespoke weight management strategies.
3. Innovative Delivery Systems Will Improve Patient Adherence
Next-generation formulations, including oral pills, transdermal patches, and implantable devices, are poised to replace traditional injections, making long-term weight management more accessible and comfortable.
4. Long-Term Safety Data Is Crucial
As new therapies emerge, rigorous clinical trials are essential to ensure safety and efficacy, especially for multi-agonist drugs that interact with multiple hormonal pathways.
5. Lifestyle Integration Remains Key
Medications like Ozempic are most effective when combined with behavioral, nutritional, and lifestyle interventions, emphasizing a holistic approach to sustainable weight loss.
Curated Expert Resources
- Nature Reviews Endocrinology: Offers comprehensive reviews on multi-agonist GLP-1 therapies and future directions, valuable for staying at the scientific forefront.
- NEJM (New England Journal of Medicine): Provides cutting-edge clinical trial data on delivery innovations and safety profiles of next-generation weight loss drugs.
- American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE): Guidelines and expert consensus on personalized approaches and advanced pharmacotherapy options.
Final Expert Perspective
The landscape of weight loss therapy in 2025 is poised for a paradigm shift, driven by innovative GLP-1 receptor agonists, personalized medicine, and advanced delivery systems. Ozempic remains a leader today, but the future promises even more effective, patient-friendly solutions. Engaging with cutting-edge research and expert resources will be essential for clinicians and patients alike. To deepen your understanding and stay ahead in this evolving field, consider exploring doctor-supervised Ozempic programs and related authoritative sources. Your proactive approach to education can make all the difference in achieving sustainable weight management success.

