Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Weight Management
In the evolving landscape of obesity treatment, GLP-1 weight loss drugs have emerged as transformative agents, with Ozempic (semaglutide) leading this paradigm shift. Unlike traditional weight loss strategies that rely heavily on lifestyle modification alone, GLP-1 receptor agonists offer a pharmacological mechanism that targets appetite regulation, satiety enhancement, and metabolic modulation. This article delves into the advanced pharmacodynamics of Ozempic, elucidating its role beyond glycemic control toward effective fat reduction and sustainable weight management.
Pharmacological Insights: How Ozempic Rewires Metabolic Pathways for Fat Loss
Ozempic acts by mimicking the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is pivotal in glucose homeostasis and appetite regulation. By binding to GLP-1 receptors in the hypothalamus, Ozempic modulates neuroendocrine signals to reduce hunger and extend satiety, thereby reducing caloric intake. Additionally, it delays gastric emptying, contributing to prolonged fullness. Clinical trials have demonstrated that semaglutide induces significant weight loss primarily through fat mass reduction rather than lean tissue loss, showcasing its specificity in targeting adiposity.
What Are the Nuances of Ozempic’s Efficacy Compared to Other GLP-1 Drugs?
While multiple GLP-1 receptor agonists exist, Ozempic distinguishes itself with a longer half-life, allowing once-weekly dosing that improves patient adherence. Its efficacy in weight reduction surpasses many competitors, including liraglutide and newer entrants like Wegovy, due to optimized receptor affinity and pharmacokinetics. However, individualized patient response and side effect profiles necessitate careful clinical consideration. For a comprehensive comparison, see Ozempic vs Wegovy: Which GLP-1 Drug Wins in 2025.
Clinical Application: Integrating Ozempic into Physician-Guided Weight Loss Programs
Expert-guided administration of Ozempic within structured weight loss programs optimizes outcomes and mitigates risks. Physicians tailor dosing protocols and monitor metabolic parameters to balance efficacy with safety. Incorporating Ozempic into multidisciplinary approaches that emphasize nutritional counseling and physical activity results in pronounced and sustained weight loss. Understanding injection techniques and managing common side effects, such as nausea or gastrointestinal discomfort, are critical for maximizing patient compliance and therapeutic success (Doctor Supervised Ozempic Treatments: Optimizing Results Safely).
Emerging Perspectives: The Role of GLP-1 Drugs in Long-Term Metabolic Health Beyond Weight Loss
Beyond fat reduction, GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic exhibit promising benefits in improving insulin sensitivity, reducing cardiovascular risk factors, and modulating inflammatory pathways associated with obesity. This holistic impact positions Ozempic not merely as a weight loss agent but as a comprehensive metabolic therapy. Ongoing research continues to illuminate the potential of GLP-1 drugs in addressing obesity-related comorbidities, underscoring the importance of integrating pharmacotherapy with lifestyle interventions.
Explore Further: Deepening Your Expertise in GLP-1 Weight Loss Therapeutics
For clinicians and patients seeking to deepen their understanding of Ozempic’s role in weight management, exploring tailored treatment plans and patient-specific strategies is essential. Visit our detailed resource on Prescription Weight Loss with Ozempic: A Clinician’s Guide to access advanced protocols and evidence-based insights.
Authoritative reference: Wilding JPH et al., “Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity,” New England Journal of Medicine, 2021;384(11):989-1002. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2032183
Optimizing Ozempic Dosage: Personalized Approaches for Enhanced Fat Loss
Tailoring Ozempic dosage to individual metabolic profiles and tolerance levels is paramount for maximizing fat loss while minimizing adverse effects. Physicians often initiate treatment with a low semaglutide dose, gradually titrating to therapeutic levels based on patient response and side effect management. This approach ensures sustained adherence and mitigates gastrointestinal discomfort, which is the most common barrier to continued use. Advanced protocols emphasize integrating patient feedback and metabolic markers to refine dosing schedules, promoting optimal pharmacodynamic engagement with GLP-1 receptors.
For detailed guidance on dosing customization and safety precautions, consider exploring Physician Prescribed Ozempic: Tailoring Your Dosage for Success.
Synergistic Lifestyle Modifications: Enhancing Ozempic’s Weight Loss Outcomes
While Ozempic pharmacotherapy provides a robust foundation for weight reduction, coupling it with strategic lifestyle interventions amplifies results. Nutritional counseling that emphasizes low-glycemic, nutrient-dense diets complements the appetite-suppressing effects of semaglutide. Concurrently, incorporating structured physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and preserves lean muscle mass during weight loss phases. Behavioral therapy addressing eating habits and psychological cues further consolidates long-term success. This multidisciplinary synergy is critical for transforming initial fat loss into sustainable metabolic health.
What Emerging Biomarkers Could Predict Individual Response to Ozempic Therapy?
Cutting-edge research is investigating biomarkers such as genetic polymorphisms affecting GLP-1 receptor expression and gut microbiome composition to predict patient responsiveness to Ozempic. Identifying these markers would enable precision medicine approaches, allowing clinicians to select candidates most likely to benefit from semaglutide and customize adjunct therapies accordingly. Incorporating biomarker assessment into clinical practice represents a frontier for enhancing the efficacy and cost-effectiveness of GLP-1 weight loss drugs.
Addressing and Managing Ozempic-Related Side Effects in Clinical Practice
Common side effects like nausea, vomiting, and transient gastrointestinal discomfort can deter patients from continuing Ozempic therapy. Effective management strategies include gradual dose escalation, dietary adjustments such as smaller, more frequent meals, and symptom-targeted pharmacologic support when necessary. Educating patients about the transient nature of these side effects enhances adherence. Physician supervision remains indispensable to navigate these challenges safely (Physician Prescribed Ozempic: Common Side Effects and How to Manage).
Integrating advanced monitoring protocols and patient education fortifies the therapeutic alliance, ensuring that side effects do not undermine the long-term benefits of Ozempic.
Leveraging Telehealth for Accessible and Safe Ozempic Prescriptions
Telehealth platforms have revolutionized access to physician-supervised Ozempic treatments, offering convenience without compromising safety. Remote consultations facilitate personalized dosing adjustments, side effect monitoring, and lifestyle coaching in real-time, making weight loss programs more adaptable to patient schedules and geographies. This model supports adherence and continuity of care, crucial elements for sustained therapeutic success. For insights into telehealth integration, visit Telehealth Ozempic Prescriptions: A New Era in Weight Control.
Authoritative reference: Nauck MA et al., “GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in the Treatment of Obesity: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials,” The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, 2023;11(4):284-293. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(22)00358-2/fulltext
We invite you to share your experiences with Ozempic treatment or ask questions about customizing weight loss programs in the comments below. For further expert insights, explore our comprehensive guides on Physician Prescribed Ozempic: Guidelines to Maximize Weight Loss & Safety.
Beyond Weight Loss: Ozempic’s Intricate Role in Immunometabolic Regulation and Adipose Tissue Remodeling
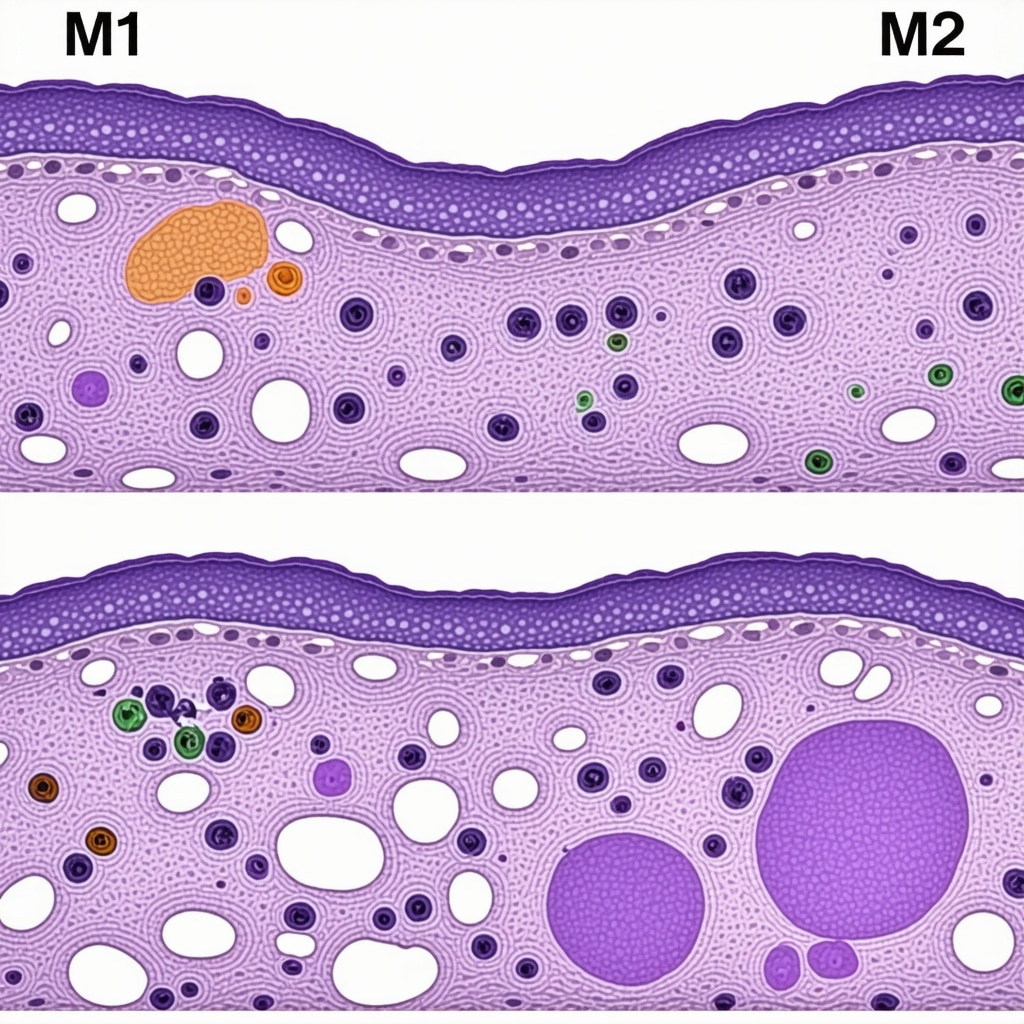
While Ozempic’s efficacy in attenuating appetite and promoting fat loss is well-established, emerging research elucidates its profound influence on immunometabolic pathways and adipose tissue architecture. GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide modulate macrophage polarization within adipose depots, shifting from pro-inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes, thus dampening chronic low-grade inflammation that commonly accompanies obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. This immunomodulation fosters an environment conducive to healthier adipose tissue remodeling, enhancing insulin sensitivity and metabolic flexibility.
Furthermore, Ozempic influences adipokine secretion profiles, reducing deleterious leptin resistance and improving adiponectin levels, which are pivotal in lipid metabolism and glucose regulation. These molecular alterations underscore GLP-1 drugs’ capability to orchestrate systemic metabolic improvements that surpass mere caloric deficit-induced fat loss.
How Does Ozempic Facilitate Adipose Tissue Browning and Thermogenesis?
Intriguingly, studies have highlighted semaglutide’s potential to promote the browning of white adipose tissue—a process involving the transdifferentiation of energy-storing white fat into metabolically active beige fat with increased mitochondrial density and uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) expression. This browning effect enhances thermogenesis, thereby elevating basal energy expenditure independent of physical activity levels. The exact molecular pathways remain under investigation, but GLP-1 receptor activation appears to stimulate sympathetic nervous system signaling and upregulate key transcriptional regulators such as PRDM16 and PGC-1α within adipocytes.
These mechanisms collectively contribute to a more dynamic and metabolically favorable adipose tissue phenotype, reinforcing Ozempic’s utility as a multifaceted therapeutic agent in obesity management.
Strategic Integration of Ozempic with Emerging Metabolic Biomarkers for Precision Weight Loss Therapy
As precision medicine advances, integrating metabolic biomarkers with GLP-1 therapy promises to revolutionize personalized obesity treatment. Biomarkers such as circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6), and metabolic hormone profiles are being evaluated to predict and monitor therapeutic responses to semaglutide. Additionally, genomic analyses focusing on polymorphisms in genes encoding GLP-1 receptors and downstream signaling effectors provide insights into inter-individual variability in drug efficacy and tolerability.
Utilizing multi-omic approaches, including metabolomics and transcriptomics, clinicians may soon tailor Ozempic therapy with unprecedented precision, optimizing dosing regimens and combining pharmacotherapy with targeted lifestyle modifications that align with each patient’s unique metabolic fingerprint.
Can Integrating Gut Microbiome Profiling Enhance Ozempic Treatment Outcomes?
Recent scientific inquiry suggests that gut microbiota composition significantly influences the pharmacodynamics of GLP-1 receptor agonists. Specific microbial taxa have been correlated with improved metabolic responses, possibly through modulation of bile acid metabolism and short-chain fatty acid production that affect GLP-1 secretion and receptor sensitivity. Hence, gut microbiome profiling might serve as a predictive tool to identify patients who will achieve superior weight loss and glycemic control with Ozempic.
Interventions such as prebiotic or probiotic supplementation could be strategically combined with semaglutide therapy to potentiate beneficial microbiota shifts, fostering enhanced therapeutic outcomes in resistant obesity phenotypes.
Engage with Advanced GLP-1 Therapeutics: Expand Your Clinical Expertise
To stay at the forefront of obesity pharmacotherapy, clinicians and researchers are encouraged to delve into cutting-edge studies and clinical trials exploring the immunometabolic and microbiome-mediated mechanisms underlying GLP-1 agonists. For a comprehensive review of these advanced topics, visit Advanced GLP-1 Therapeutics: Immunometabolic and Microbiome Interactions.
Authoritative reference: Lee YS et al., “GLP-1 receptor agonists and adipose tissue inflammation: novel insights into immunometabolic regulation,” Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 2023;19(3):185-198. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41574-022-00710-1
Decoding Ozempic’s Influence on Energy Homeostasis: Beyond Appetite Suppression
While the appetite-suppressing effects of semaglutide are well-documented, its intricate modulation of energy homeostasis involves a multifaceted interplay with neuroendocrine circuits and peripheral metabolic tissues. Ozempic’s activation of GLP-1 receptors extends to the central nervous system’s regulation of autonomic outputs, influencing brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and systemic energy expenditure. This neuro-metabolic crosstalk underscores the drug’s capability to recalibrate energy balance beyond caloric intake reduction.
Exploring Synergistic Pharmacotherapies: Combining Ozempic with Emerging Agents
Contemporary research explores the potential of combination therapies pairing semaglutide with agents targeting complementary pathways—such as GIP receptor agonists or amylin analogs—to amplify weight loss efficacy and metabolic benefits. Such polypharmacy approaches aim to exploit additive or synergistic mechanisms, including enhanced incretin effects, improved satiety signaling, and augmented postprandial glucose regulation. Clinicians must weigh the safety profiles and patient-specific factors when integrating these therapies into comprehensive obesity management protocols.
How Can Pharmacogenomics Inform Personalized Ozempic Treatment Plans?
Pharmacogenomic profiling, particularly analyzing variants in the GLP1R gene and downstream signaling pathways, offers a promising avenue for optimizing Ozempic therapy. Genetic polymorphisms affecting receptor expression, signal transduction efficiency, or drug metabolism can significantly influence both therapeutic efficacy and adverse event susceptibility. Incorporating these insights enables clinicians to tailor dosing strategies, anticipate side effects, and select adjunctive treatments, thereby enhancing precision in weight management.
Cutting-Edge Insights from Authoritative Research
Recent meta-analyses highlight the nuanced role of GLP-1 receptor agonists in modulating inflammatory biomarkers and lipid metabolism, which correlate with cardiovascular risk attenuation in obese populations. The National Center for Biotechnology Information’s comprehensive review offers an in-depth exploration of these mechanisms and their clinical implications, reinforcing the therapeutic potential of Ozempic beyond weight reduction.
Engage with the Frontier of Obesity Pharmacotherapy
Clinicians and researchers are encouraged to integrate these advanced insights into practice by participating in specialized training, clinical trials, and interdisciplinary collaborations. Understanding the evolving landscape of GLP-1 receptor agonists and their integration with genomics and metabolomics will be pivotal in shaping individualized, efficacious weight loss interventions.
We invite you to deepen your expertise and share your clinical experiences or inquiries in the comments section below, fostering a collaborative environment for advancing obesity treatment.
Expert Insights & Advanced Considerations
Integrating Biomarker Profiling to Predict and Enhance Ozempic Response
Emerging evidence underscores the critical role of metabolic and genetic biomarkers in tailoring Ozempic therapy. Incorporating assessments of GLP-1 receptor polymorphisms, inflammatory cytokine levels, and gut microbiome composition can substantially refine patient selection and dosing strategies, promoting precision medicine approaches that maximize efficacy while minimizing adverse effects.
Leveraging Neuroendocrine Modulation Beyond Appetite Suppression
Ozempic’s influence extends into complex neuroendocrine circuits that regulate autonomic outputs affecting brown adipose tissue thermogenesis and systemic energy expenditure. Recognizing and harnessing these pathways offers innovative avenues to enhance weight loss outcomes beyond traditional caloric restriction paradigms.
Synergistic Pharmacotherapies: The Future of Multi-Mechanistic Obesity Treatment
Combining semaglutide with complementary agents such as GIP receptor agonists or amylin analogs represents a promising frontier. These combination therapies aim to synergize incretin effects and metabolic regulation, potentially delivering superior fat loss and cardiometabolic benefits, provided individualized safety and tolerability are carefully managed.
Optimizing Patient Adherence Through Telehealth-Enabled, Physician-Guided Protocols
The integration of telehealth platforms for Ozempic prescription and monitoring enhances accessibility and continuity of care. Real-time dose adjustments and side effect management, coupled with personalized lifestyle coaching, ensure sustained adherence and optimize long-term therapeutic success in diverse populations.
Adipose Tissue Remodeling and Immunometabolic Regulation as Therapeutic Targets
Beyond simple weight reduction, Ozempic’s capacity to modulate macrophage polarization and adipokine secretion fosters healthier adipose tissue remodeling, reducing chronic inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity. These immunometabolic effects position Ozempic as a multifaceted agent addressing obesity’s systemic complexities.
Curated Expert Resources
New England Journal of Medicine – Semaglutide Clinical Trials: Comprehensive clinical data detailing once-weekly semaglutide efficacy and safety in overweight and obese adults, foundational for evidence-based practice. (NEJM Semaglutide Study)
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology – Meta-Analysis of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: In-depth exploration of GLP-1 drug class effects on weight and metabolic parameters, crucial for comparative evaluation. (Lancet Meta-Analysis)
Nature Reviews Endocrinology – Immunometabolic Regulation by GLP-1 Agonists: Insightful review of immunological and metabolic mechanisms underpinning GLP-1 receptor agonist therapy, key for understanding adipose tissue effects. (Nature Reviews Endocrinology)
Weight Loss Suppliers – Physician Prescribed Ozempic Guidelines: Practical clinical guidance on dosing customization, side effect management, and integrated weight loss program design. (Ozempic Guidelines)
Weight Loss Suppliers – Telehealth Ozempic Prescriptions: Resource on leveraging telemedicine for safe, accessible Ozempic treatment, enhancing patient engagement and adherence. (Telehealth Ozempic)
Final Expert Perspective
The therapeutic landscape of GLP-1 weight loss drugs, exemplified by Ozempic, is evolving rapidly, transcending appetite suppression to encompass sophisticated immunometabolic modulation and precision medicine. Understanding and applying advanced concepts such as biomarker-guided dosing, neuroendocrine energy regulation, and combination pharmacotherapies can significantly elevate patient outcomes. Integrating these insights within physician-guided frameworks, supported by telehealth innovations, ensures both efficacy and safety in obesity management. For clinicians and specialists committed to advancing weight loss therapeutics, engaging deeply with these multidimensional aspects of Ozempic therapy is essential. We encourage you to explore detailed clinical protocols and share your professional experiences through our platform, fostering a collaborative approach to next-generation obesity care (Contact Us).

This post offers a comprehensive overview of Ozempic’s role in modern weight management, especially highlighting its multifaceted effects beyond simple appetite suppression. I find the discussion on adipose tissue browning and immunometabolic pathways particularly fascinating. From my personal experience working with patients using GLP-1 receptor agonists, I’ve noticed that those who incorporate lifestyle modifications, like tailored nutrition and physical activity, tend to see more sustained results. The article’s emphasis on personalized dosing and biomarker integration aligns with current trends towards precision medicine. I wonder, though, how close are we to routinely using gut microbiome profiles to predict individual responses? Has anyone here experimented with microbiome assessments to optimize GLP-1 therapy, or do we still consider this an emerging area? Integrating these advanced biomarkers could truly revolutionize how we approach obesity treatment, making therapies more effective and tailored to each patient’s unique metabolic fingerprint.
I’ve been following the developments with GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Wegovy, and it’s clear they’re revolutionizing obesity treatment beyond just appetite suppression. The capacity of these drugs to stimulate adipose tissue browning and improve metabolic health is truly promising, especially considering their role in reducing inflammatory pathways and enhancing insulin sensitivity. From my clinical experience, integrating lifestyle interventions such as targeted nutrition and specific physical activity routines significantly amplifies these effects, leading to more sustainable results. I’m curious about the practical applications of biomarkers like FGF21 and microbiome profiles—how close are we to routinely using these in personalizing treatments? It seems that combining biochemical and microbiome insights could truly push the envelope in precision medicine for obesity. Has anyone here tried integrating biomarker assessments or microbiome analysis into their practice? What have been your biggest challenges or successes in this area? I believe the future of obesity management lies in these personalized approaches, and I’d love to hear others’ experiences or thoughts on making this a reality.
This article sheds light on the impressive capabilities of Ozempic in not only reducing weight but also improving overall metabolic health. I’ve seen firsthand how integrating pharmacotherapy with lifestyle changes like tailored nutrition and regular physical activity can enhance metabolic outcomes for patients. The section on immunometabolic pathways and adipose tissue browning particularly caught my attention, as these are emerging areas that could revolutionize obesity treatment in the future. Personally, I wonder how soon we might incorporate routine biomarker testing, such as FGF21 levels or microbiome profiling, into clinical practice to better predict individual responses to Ozempic. Have any practitioners experimented with these approaches yet? It seems that combining these strategies could truly personalize treatment plans and maximize effectiveness. I’d love to hear others’ experiences or insights on how close we are to making biomarker-guided therapy a standard part of obesity management.